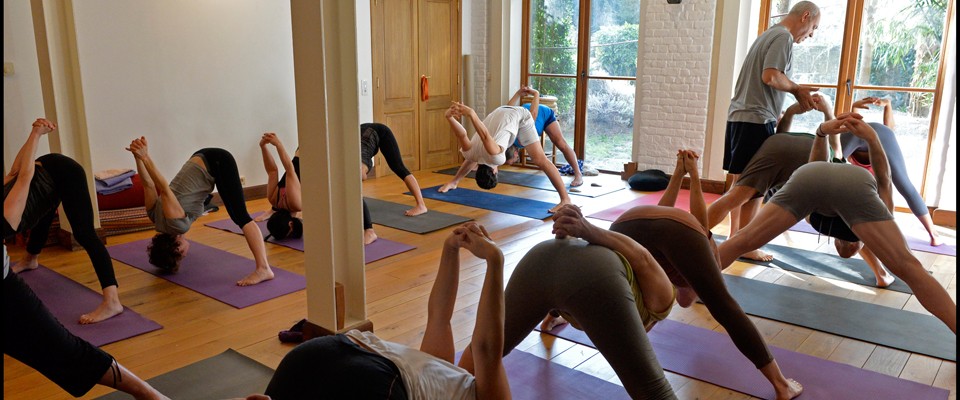
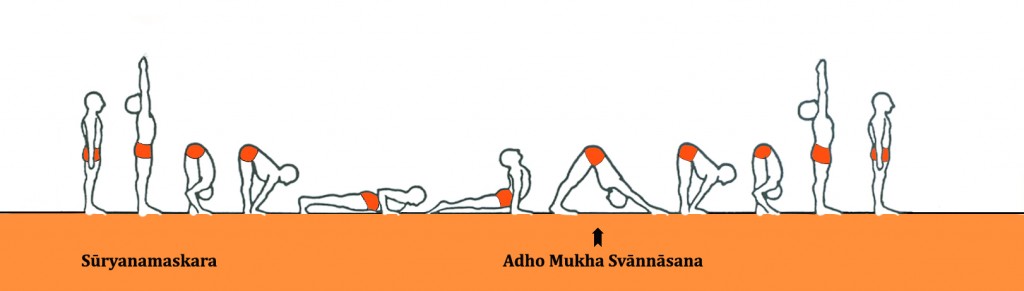
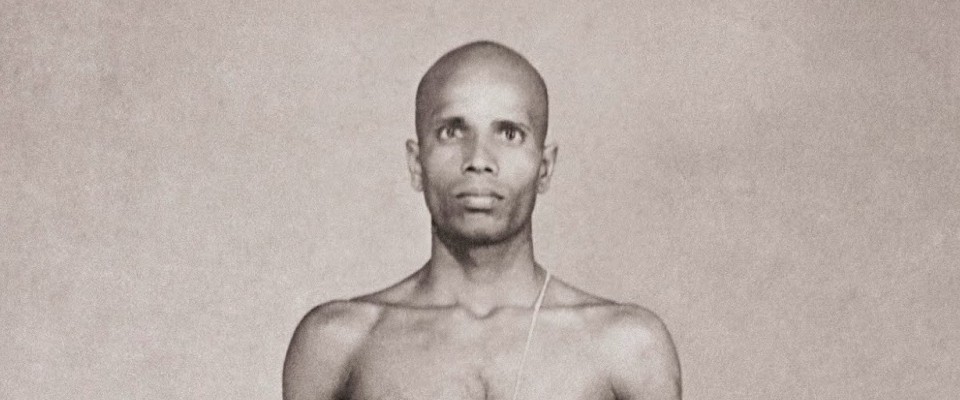
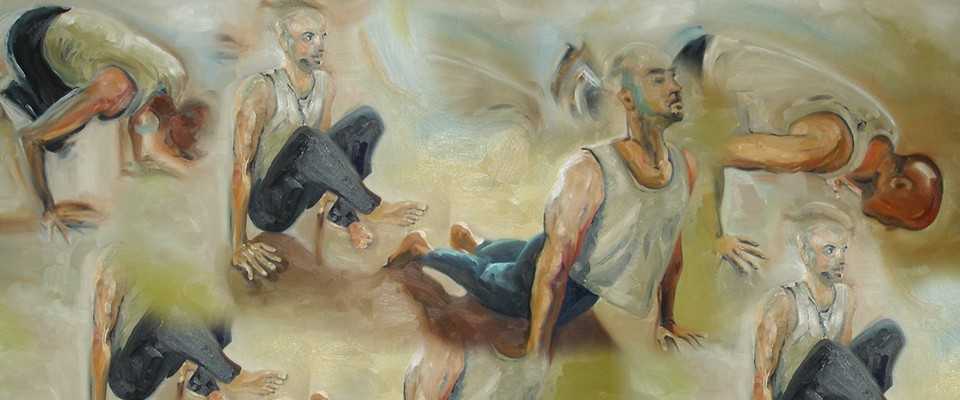The Ashtanga Yoga Institute in Brussels perpetuates the teachings of Sri K. Pattabhi Jois. Since 1973, Jean Claude Garnier trains students, in Europe and Asia, to deepen their knowledge about Yoga. Some of the students will find a calling and become a Yoga Professor and in turn, transmit the art of Yoga.
The Institute is open to different currents of Yoga. Jean Claude Garnier pursues the transmission of Ashtanga Yoga as taught by Krishnamacharya and his disciples B.K.S. Iyengar, and Sri K. Pattabhi Jois.

Sri K. Pattabhi Jois
Training and recycling as a Yoga professor, who is concerned ?
- People who practice Yoga and wish to deepen their self-knowledge in order to obtain a better body and mind balance
- Those who wish to deepen their approach of the tradition of Yoga
- Future teachers who wish to teach Yoga in Europe – this requires a commitment to a course of minimum 5 modules
- Existing Yoga teachers who wish to broaden their personal knowledge with an ancient and dynamic method
- Yoga teachers who have the obligation to improve and develop their existing skills
How does the training with personal monitoring take place ?
- You deepen your knowledge of the practice of Yoga: first, second and third series
- You study Yoga and its philosophy
- You learn to observe during classes (group and private classes)
- You progressively assist the teacher during classes
- You will be supervised as of your first class, in order to answer your questions.
How to obtain a diploma
The Yoga teacher training consists of a set of modules.
At the end of each module there is a practical and theoretical evaluation.
Once you have successfully passed a module, you can move on to the next one.
You need to complete a minimum of 5 modules (A, B, C, D, E, F) and write a thesis which summarizes your studies and research on one of the aspects of Yoga.
This diploma is a requisite to :
- Practice the profession in European countries
- Teach in a recognised Institute
- Register to the national professional database
- Get an insurance
- As an asset for your students
European PDF laws
European Yoga Union: http://www.yogaeurop.com/index.php?categoryid=21

Proto Shiva, of the Indus civilization
Content covered during the training
Theoretical documentation will be given to you at the end of each module in electronic version (with an access to “training”)
Topics
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Psychology
- Pedagogy
- Professional ethics
- History
- Etymology
- Indian sacred texts
Also discussed: communication, oral and written expression, dietetics, lifestyle…
Course content of Training Module A
- Postural practice first & second series (Sádhaná Yoga)
Postural foundations, supports, reviewing and improvement of postures and their variations; breathing techniques in postures (pranayama); development of concentration, letting go, individual work and group work, workshops, first trials of teaching.
-

-
Brussels, Ashtanga Yoga Teacher Training
-

-
Brussels, Ashtanga Yoga Teacher Training
-

-
Brussels, Ashtanga Yoga Teacher Training
-

-
Brussels, Ashtanga Yoga Teacher Training
Theoretical courses
- Classical Indian Tradition through its Vedic origins
- Invocations (prayer at the beginning of the class): explanation, its significance and its meaning.
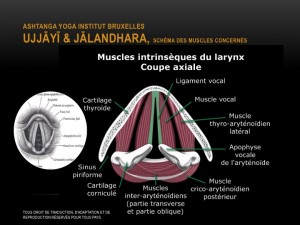
- Theory and practice of Ashtanga Yoga (Mula Bandha, uddiyana, Ujjayi Pranayama, Vinyasa)
- Knowledge of anatomy related to postural practice
- Importance of stretching during Yoga postures
- Use of Sanskrit during courses
- Religious festivals
- The creation of the world (Taittiriya Aranyaka viewed by Veda)
- The life, work and education of Sivananda, Sri Ramakrishna, Swami Ramdas, Yogi Ram Surat Kumar, Sri Yukheswar, Alain Danielou, Krishnamurti.
Check the PDF files to see the content of the other training modules
Admissions
The admission procedures are common to all schools of the National Federation of Yoga Teachers
To enrol in the first year of training you must:
- Have practiced Yoga for at least 2 years with one or more teachers and have one of the teachers complete a sponsorship record
- Be over 18 years old
- Have a general level of education or equivalent vocational training at high-school level.
When and where:
- India: the longest training (one month)
- Greece: condensed training (two weeks)
- Belgium: all year long (10 weekends from September to June / July)